Background/Aims: The interaction of CD40 ligand (CD40L) and CD40 triggers the induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines. It has been proposed that vitamin D deficiency might be an important factor, which causes or aggregates the autoimmune situations. The aim of the present study was to assess the effect of vitamin D on CD40L gene expression in patients with ulcerative colitis (UC).
Materials and Methods: Ninety mild-to-moderate UC patients were randomized to receive a single injection of 7.5 mg cholecalciferol or 1 mL normal saline. At baseline and 90 days following the intervention, RNA samples from whole blood were obtained. Fold changes in CD40L mRNA expression were determined for each patient using the 2-ΔΔCq method. The data were analyzed.
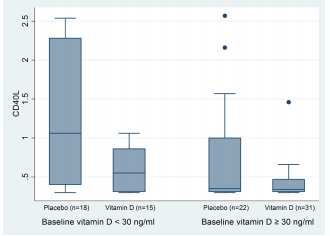
Results: The serum levels of vitamin D and calcium increased only in the vitamin D group (p<0.05). Relative to baseline values, the CD40L gene expression fold change was significantly lower in the vitamin D group compared with the placebo group (median±interquartile range: 0.34±0.30 vs 0.43±1.20, respectively, p=0.016).
Conclusion: The results of this study showed that vitamin D administration in mild-to-moderate UC patients led to the downregulation of the CD40L gene, which is an essential part of inflammatory pathways.
Cite this article as: Sharifi A, Vahedi H, Honarvar Reza M, Amiriani T, Nikniaz Z, Rad Yousefi E, Hosseinzadeh-Attar Javad M. Vitamin D decreases CD40L gene expression in ulcerative colitis patients: A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Turk J Gastroenterol 2020; 31(2): 99-104.




.png)
.png)