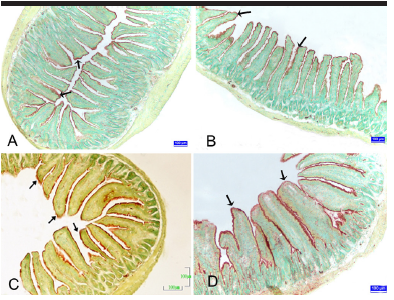
Background/Aims: The aim of the present study was to determine the changes on the small intestine in mice during pregnancy using histological, enzyme histochemical, and immunohistochemical methods.
Materials and Methods: A total of 24 Swiss albino female mice were divided as non-pregnant/control, first week, second week, and third week of pregnancy (n=6). Tissue samples obtained from the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum were processed by means of routine histological techniques and stained with Crossmon’s triple staining. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) was demonstrated with the simultaneous azo-coupling method. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) was demonstrated with the streptavidin-biotin-peroxidase complex method. The numerical data of the parameters were obtained and analyzed statistically.
Results: Villus height, villus width, and the rate of villus height/crypt depth were decreased in the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum in the last week of pregnancy compared with the control group. Changes in the crypt depth of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum in pregnancy were found. The muscle width increased in pregnancy. It was identified that the ALP reactivity statistically significantly increased in the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum in pregnancy. The percentage of PCNA-positive cells in the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum increased in the first and second weeks of pregnancy, whereas it decreased in the third week of pregnancy compared with non-pregnant control animals.
Conclusion: In conclusion, villus parameters, ALP reactivity, and percentage of PCNA-positive cells in the small intestine were affected during pregnancy.
Cite this article as: Şensoy E, Öznurlu Y. Determination of the changes on the small intestine of pregnant mice by histological, enzyme histochemical, and immunohistochemical methods. Turk J Gastroenterol 2019; 30(10): 917-24.




.png)
.png)